
The Power of Parallel Generators: Enhancing Capacity and Control
Understanding Parallel Generators
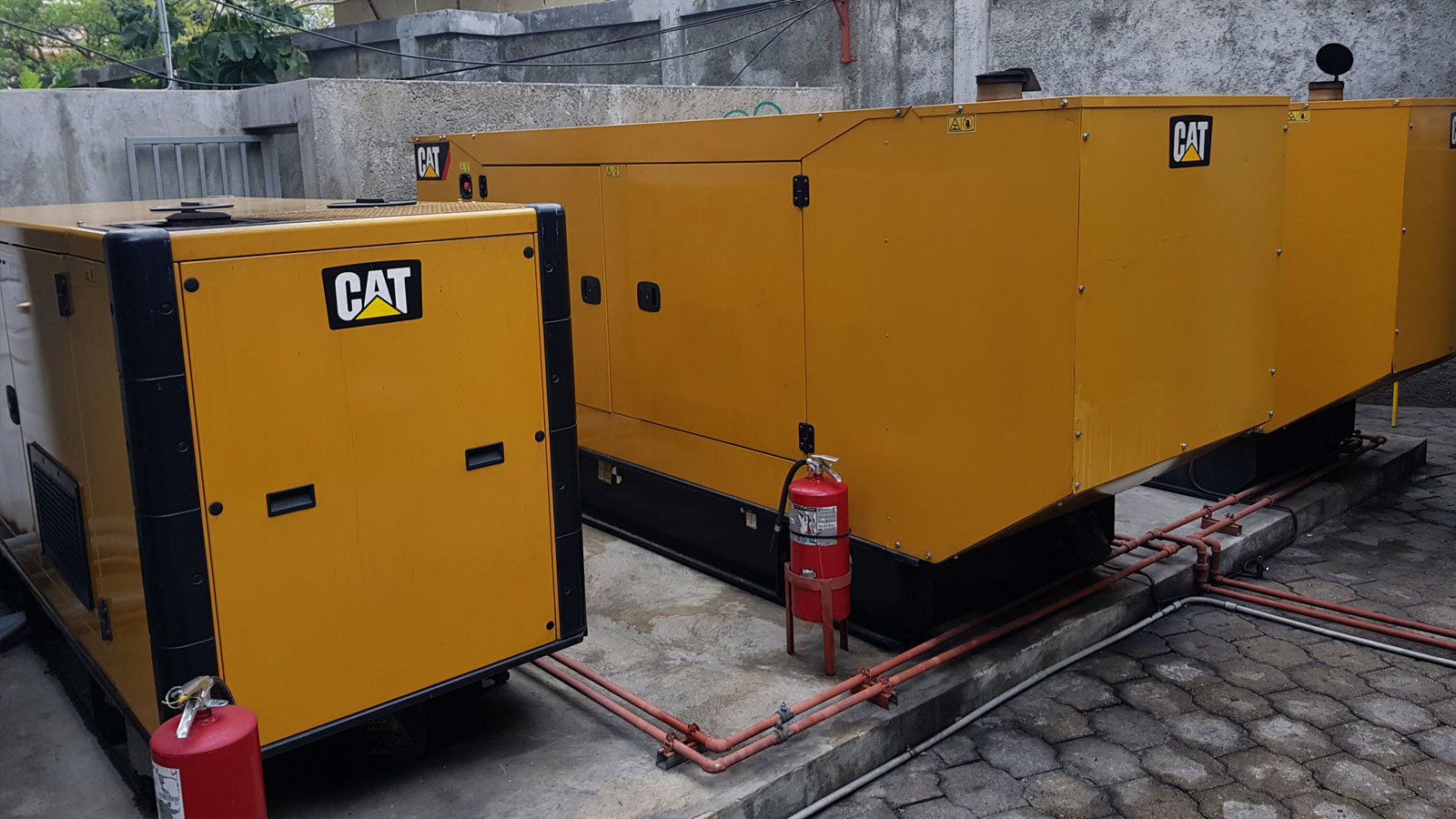
In the world of electric generators, ‘paralleling’ is not just a buzzword but a strategic approach to power management. At its core, connecting generators in parallel involves physically linking two or more generators and synchronizing their outputs. But why is this approach gaining traction, and what benefits does it hold?

The synchronization matches the waveform of the output voltage of one generator with the voltage waveform of the other generator (s).
1. Boosted Power Capacity
The most straightforward advantage of paralleling generators is the increase in power capacity. Instead of being limited to the output of a single generator, users can harness the combined power of multiple units. This is especially useful in large facilities, events, or areas with high power demands, ensuring that the power supply meets the demand without a hitch.
2. Precision in Load Management
With multiple generators working in tandem, it’s easier to manage and distribute loads. This means that during periods of lower power demand, not all generators need to run at full capacity. This modulated approach can lead to fuel savings and reduce wear and tear on the generators.
3. Ease of Maintenance
With a parallel system, maintenance becomes a less disruptive process. If one generator requires servicing or repairs, the others can continue operating, ensuring a continuous power supply. This also means that there’s no rush during maintenance, allowing for thorough checks and reducing the risk of downtime.
4. Built-in Redundancy
One of the significant benefits of paralleling generators is redundancy. If one generator fails or faces issues, the others can pick up the slack. This redundancy ensures that there’s always a backup, minimizing disruptions and providing a consistent power flow.
5. Synchronization: The Heart of the Process
The process’s success hinges on precise synchronization. This involves aligning the frequency, phase, and amplitude of the electrical outputs from all generators. Modern control systems and technologies have made synchronization more accessible and accurate, ensuring that all generators work in perfect harmony.
Conclusion
The strategy of connecting generators in parallel represents a paradigm shift in power management. With its myriad benefits, from increased capacity to built-in redundancy, it’s no wonder that facilities worldwide are adopting this approach. As our energy needs grow and evolve, strategies like these will be crucial in ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply.







GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings